
Investment in Indonesia’s New Capital City
Relocation of Indonesia’s New Capital City: Current Developments and Incentives for Investors
The Province of DKI Jakarta has been the capital city of Indonesia for 63 (sixty) years since the enactment of Law No. 2/1961 and PD No. 2/1961 . Initially named as Jakarta Raya, it was then changed to ‘Jakarta' on 31 August 1964 by the enactment of Law No. 10/1964. Regardless the enactment of such regulations, the idea of moving the capital city has always been on the table since Soekarno’s presidency era in 1957 until Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono’s presidency era due to extensive flooding and unfavourable traffic issues in Jakarta.
Following the prolonged discourse, the Government of Indonesia finally realized such plan during Jokowi’s presidency through the enactment of RPJMN 2020-2024. The RPJMN 2020-2024 is part of Indonesia’s 2045 vision by targeting the ability to pass the ‘middle income trap’ as a nation.
As reflected from RPJMN 2020-2024, the establishment of capital city out of Java Island is considered as a fair approach in terms of spatial and economic growth, as an economic stimulus to push the economic diversification of Kalimantan Island, source of new and sustainable economic growth for Kalimantan Island and easter regions of Indonesia, and to negate the inequality between regions, through smart governance policies.
Aligned with the government’s updated policy direction, the RPJMN 2025–2029 reaffirms the continuation of the new capital city development under Priority Program 3, which focuses on advancing national infrastructure development. Its first target emphasizes achieving sustainable, integrated, and equitable infrastructure across regions. Accordingly, the establishment and development of the new capital city remain on track as part of the government’s long-term strategy to create new growth centers, reduce regional disparities, and support Indonesia’s broader economic transformation toward the 2045 vision
The plan then further contextualized by the promulgation of Law 3/2022 which specifically established Indonesia’s Capital City named IKN – located in East Kalimantan province – and IKN Authority on 15 February 2023. On November 30, 2024, pursuant to Law 2/2024, the Province of the Special Capital Region of Jakarta was redesignated as the Province of the Special Region of Jakarta. This regulation marks the official migration of status, function, and duties of capital city from DKI Jakarta to IKN.
Further, the development and transfer of IKN is regulated under the Master Plan of IKN which are divided into 5 (five) stages. It is further regulated through GR 17/2022 that the preparation, establishment, and migration of IKN shall at least be established as part of national priority program for minimum of 10 (ten) years of the Government of Indonesia’s work plan since 2022 or at least until the completion of the 3rd stage of IKN’s construction. In essential, the construction stages as elaborated by the Master Plan of IKN are as follows:

Investment on Indonesia’s New Capital City
Source: PR No. 63/2022.
The development of IKN has entered its second phase for the 2025–2029 period. This phase focuses on constructing public transportation facilities, expanding residential areas, completing the relocation of civil servants, and continuing as well as maintaining existing infrastructure. The developments include 800–850 hectares of the Central Government Core Area, reaching 20% progress for government buildings, 50% completion of housing, 50% availability of basic infrastructure, and achieving an accessibility and connectivity index of 0.74 for the IKN area.[
Furthermore, through PR 79/2025, the government affirms the target of establishing IKN as the Political Capital by 2028, supported by the relocation of civil servants and the provision of adequate infrastructure. Under said regulation, it is targeted that between 1,700 and 4,100 civil servants will commence duty in IKN on a phased basis, with the total number projected to reach 9,500 personnel stationed in the IKN by 2029. As of September 2025, to support the relocation process, 44 residential towers are ready for occupancy, while three towers are in the completion phase and an additional four towers remain under construction.
In line with the objectives of Indonesia’s capital city migration to IKN as elaborated above, the Government has also issued regulations to govern the implementation of IKN establishment pertaining to institutional landscape in IKN, investment opportunity and incentives provided to both domestic and foreign investors in IKN, and other facilities given by the Government of Indonesia to encourage both investors and residential growth in IKN, as elaborated further in this Chapter.
Institutions Overview in IKN
The government administrators for IKN region, namely the IKN Authority, has functions to regulate and administer regional government function based on the prevailing laws, which are not limited to the execution of preparation, establishment, relocation, and management of IKN. The IKN Authority is led by the Head of IKN Authority and assisted by Vice Head of IKN Authority which are appointed and dismissed directly by the President after conducting consultation with the House of Representative of the Republic of Indonesia. However, for the first Head and Vice Head of IKN Authority after the enactment of Law 3/2022 were appointed before the consultation with the House of Representative as the inauguration shall be done in 2 (two) months after the enactment of such law. As of now, the appointed Head of IKN Authority is Dr. (H.C.) Ir. H. M. Basuki Hadimuljono, M.Sc., Ph.D.
The appointment mechanism for the Head and Vice Head of IKN Authority is different from the ordinary appointment mechanism of the other head regions. The Head and Vice Head of IKN Authority hold the title for 5 (five) years since the inauguration date and can be re-appointed for the same period, and they may also be dismissed by the President during their tenure.
The IKN Authority is vested with special authorities on administering central and regional governmental matters in preparation, establishment, relocation, and management of IKN. These special authorities also include, among others, authority in granting investment permit, ease of business, as well as providing special facilities to the parties who support the financing in preparation, establishment, migration of IKN, as well as development of IKN and Partner Regions of IKN. To implement its special authorities, the IKN Authority shall stipulate regulation of Head of IKN Authority on the norm, standard, procedure, and criteria of preparation, establishment, relocation, and management of IKN.
The activities of preparation, establishment, relocation, and management of IKN are coordinated and conducted by the IKN Authority by taking into consideration the Master Plan of IKN. To support such activities, the support from the ministries/institutions might be required in conformity with its duties and functions, which might also include financing which are required for preparation, establishment, relocation, and management of IKN deriving from ABPN through the ministries/institutions expenses scheme. The State Property (BMN) resulted from the ministries/institutions on preparation, establishment, relocation, and management of IKN can be handed over to the IKN Authority except stated otherwise by the MoF.
Investment Opportunities in IKN
To support the preparation, development, relocation, and administration of IKN, the Government synergizes funding from the state budget and other legitimate sources under the provisions of applicable laws and regulations. In accordance with Law No. 3/2022 jo. GR No. 17/2022 jo. IKN Authority CL No. 01/2022, such sources of fund are as follows:
-
APBN (Government budget allocation/financing);
-
PPP to support IKN, which may be implemented through:
-
user charge PPP projects, where the private party generates return on investment in the form of user payment;
-
availability payment PPP projects, where the private party generates return based on availability payment sourced from the state budget of the relevant;or
-
PPP with other return on investment form in accordance with laws and regulations.
-
-
business entity participation scheme, where all or part of the capital is owned by the state, including BUMN or purely private entities, such as:
-
BUMN that collaborate with private entities through their investment;
-
BUMN assigned by the Government under laws and regulations;
-
private entities that invest in wholly private investment, which may receive incentives according to applicable laws and regulations; and
-
strategic cooperation based on an agreement between the special SOE of the IKN Authority and other relevant investment partners.
-
-
international funding/finance support scheme, which is a scheme to accommodate fund contributions, among others, from bilateral/multilateral institutions willing to participate in the green and smart development of IKN. This may be conducted through grants and/or advance funding (dana talangan);
-
utilization of Government assets, among others, through means of lease, utilization cooperation, build-operate-transfer, or build-transfer-operate; and
-
other funding schemes (creative financing), such as crowdfunding, philanthropic funds, corporate social responsibility contribution, as well as carbon trading.
It is worth nothing that while there are regulations which generally applies to all PPP projects in Indonesia, the Government has issued specific regulations for PPP projects in IKN (“IKN PPP”). These regulations are, among others, MoNDP Reg. No. 6/2022, NPPA Reg. No. 1/2023, and MoF Reg. 220/2022.
In accordance with the above list, it may be concluded that private entities (e.g. businesses and financiers) may involve themselves in the development of IKN by: (i) participating in PPP projects; (ii) cooperating with BUMN; (iii) business-to-business (purely private) investment activities; (iv) cooperating with Special BUMN of the IKN Authority; (v) providing grants and/or advance funding; and (vi) partaking in creative financing activities.
In addition, IKN Authority CL No. 1/2022 provides information on the potential investment sectors in IKN, which are as follows:
-
Central Governance Area
-
basic infrastructure: (i) drinking water provision; (ii) liquid waste management; (iii) solid waste management; (iv) provision of natural water; and (v) housing;
-
energy development: (i) solar power development; and (ii) floating solar power plant development in Sepaku Semoi;
-
transportation: (i) bus rapid transit system; (ii) intelligent transport and transit system; and (iii) urban logistics (angkutan barang perkotaan).
-
-
Regional infrastructure, which includes transportation infrastructures such as: (i) IKN toll road; (ii) airport express line; (iii) Kariangau and Semayang port development; and (iv) Sepinggan airport development.
-
Industrial and Economic
-
smart city and digital hub: (i) industry 4.0 for existing sectors; and (iv) smart city technology development;
-
education: (i) vocational high school; (ii) STEM institutions; and (iii) 12 years education;
-
sustainable agriculture: (i) plant protein; (ii) plant extraction; and (iii) herbal products and nutrition;
-
integrated pharmacy: (i) active pharmaceutical ingredient; and (ii) biosimilar.
-
ecotourism and inclusive fitness tourism: (i) ecotourism and fitness tourism; (ii) nature and wildlife tourism; (iii) urban tourism/multi-purpose hotels; and (iv) health tourism;
-
advanced chemical industry: (i) petrochemicals; and (ii) oleochemical;
-
renewable energy: (i) assembly of solar cells; and (ii) assembly of electric two-wheeler vehicles;
-
low-carbon energy: (i) biofuels; (ii) electrification, digitalization, and mining rehabilitation; and (iii) coal gasification and original equipment manufacturer.
-
Moreover, several sectors are cited as priority investment in IKN’s central governance area: (i) international hospital; (ii) integrated education facilities; (iii) business and services districts; (iv) mixed commercial and trade sector; and (v) residential facilities.
On July 11, 2024, the Government enacted PR 75/2024 in order to escalate the development of IKN. The implementation of the accelerated development of IKN aims to create a liveable city ecosystem, particularly in the Core Government Area, which includes the provision and management of basic and/or social services as well as commercial facilities. The Core Government Area is a part of the city area within the urban core of the national strategic area of IKN, serving the primary function as the centre of national Government. The provision and management of basic and/or social services, include:
-
housing;
-
healthcare
-
education;
-
social and cultural services;
-
energy and electricity;
-
telecommunications and digitalization;
-
transportation;
-
drinking water;
-
sanitation and waste management;
-
emergency facilities;
-
public cemeteries;
-
green open spaces;
-
sports facilities;
-
religious facilities;
-
office facilities; and
-
public order and security.
The provision of commercial facilities includes:
-
hotels;
-
shopping centres, retail stores, and shops;
-
restaurants; and
-
recreational and entertainment centres.
Licensing Requirements and Compliance
Business Licensing are granted by the IKN Authority to the business actors who would commence and run its business in IKN and Partner Regions, in which its licensing process is done in integrated system of OSS in conformity with the prevailing laws. Further, business actors who will commence and conduct its business in IKN and Partner Regions shall fulfil (i) basic requirements for Business Licensing; and/or (ii) sectoral Business Licensing. The basic requirements shall include (i) conformation to spatial utilization activity; (ii) environmental compliance approval; and (iii) approval of building and worthiness certificate for the building. Meanwhile, the applicable sectors for Business Licensing are as follows:
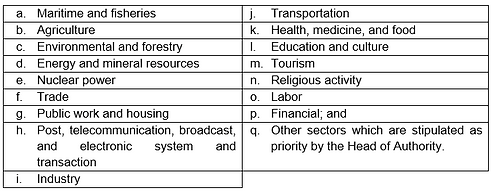
Verification on basic requirements for Business Licensing and/or sectoral Business Licensing for certain risk level in IKN shall be done by the IKN Authority, which can be delegated to institution or certified and accredited experts. Further, simplification and modernization of Business Licensing system to support acceleration of approval to basic requirement Business Licensing and/or sectoral Business Licensing may be conducted. However, there has been no implementing regulation in regards to such.
Further, business actors who intend to commence and conduct its business in IKN and Partner Regions are not required to have confirmation status as taxpayer beforehand. This is part of the incentive given by the Government as the requirement of taxpayer registration proof is part of the essential data completion that needs to be fulfilled by the business actors who intend to submit Business Licensing request.
Additionally, foreign investors are also being given wider opportunity to penetrate IKN’s investment scheme. As understood and regulated through PR 10/2021, the government has established the positive list of foreign investors and stated business sectors which are considered as ‘closed’ for foreign investors. However, the Government of Indonesia provides incentive provided to the foreign investors is the leniency given in regard to limitation of foreign capital ownership for certain business fields, specifically for business licenses issued for business activities in IKN and Partner Regions. As of now, the implementing regulation for this particular incentive is not yet enacted.
Specifically, Business Actors who carry out the development, provision, and management of basic and/or social services, as well as commercial facilities, may be granted incentives and business licensing facilities by the Head of the IKN Authority, Ministries/Agencies, and/or Regional Governments in accordance with the provisions of the applicable laws and regulations.
Investment Facilities in IKN
Investment facilities in IKN and Partner Regions are regulated under GR 12/2023. The following sub-chapter will focus on the types of investment facilities in IKN which are in the forms of fiscal and non-fiscal incentives that in accordance with the authorized institutions are divided as follows:

Types of Investment Facilities in IKN
Source: GR No.12/2023.

The MoF will grant the relevant facilities as stated above. The relevant taxpayers shall submit an application through the OSS system or other relevant electronic system provided by MoF.
The details of each facility under Article 25 (1) GR 12/2023 will be described below:
Income Tax Facilities
The income tax facilities in IKN shall be in the form of following activities, namely:
-
deduction of corporate income tax for:
-
domestic corporate taxpayers;
-
income tax facility on financial sector activities in the financial center;
-
the establishment and/or transfer of head office and/or regional office;
-
deduction of gross income for:
-
the organization of work practice, apprenticeship, and/or learning activity in the context of fostering and developing certain competency-based human resources;
-
certain research and development activities;
-
donation and/or costs for the development of public facilities, social facilities, and/or other non-profit facilities;
-
Article 21 of income tax (PPh Pasal 21) to be borne by the government and categorized as final tax;
-
final income tax of 0% (zero percent) on income from the gross turnover of certain business of micro, small, and medium scales enterprises; and
-
deduction of income tax on the transfer of land and/or building rights.
Below are the details of each type of income tax facility which specifically related with investment activities and business actors, namely:
-
Deduction of Corporate Income Tax of Domestic Corporate Taxpayers
In essence, the requirements for the domestic corporate taxpayers to obtain deduction of the corporate income tax in IKN are as follows:
-
the minimum investment shall be in the value of Rp10,000,000,000.00 (ten billion Rupiah); and
-
the business sectors conducted are those that may accelerate the construction and development of IKN, namely public infrastructure and services, economic growth, and other business sectors which might be deemed necessary.
The period of the imposition of the deduction of corporate income tax and the relevant deduction are as follows:
Period of The Imposition of The Deduction of Corporate Income Tax and The Relevant Deduction
Source: GR 12/2023
Below are the details of each business sectors:


The Business Sectors Entitled to Deduction of Corporate Income Tax of Domestic Corporate Taxpayers
Source: GR No.12/2023.
The amount of the corporate income tax deduction for the above business sectors is 100% (one hundred percent) of the total payable corporate income tax from 2023 until 2045, in which the period of deduction depends on the year of investment is being made. However, the corporate income tax deduction for Other Business Sectors which would be commenced since 2031 can only be granted for 50% (fifty percent) of the total payable corporate income tax.
-
Deduction of Corporate Income Tax on Financial Sector Activities in the Financial Centre
The income tax facilities for the relevant taxpayers that operate financial business activities in the financial center at IKN are as follows:
-
for domestic corporate taxpayers and permanent establishment, the deduction for corporate income tax is ranging between 85% (eighty-five) percent to 100% (one hundred) percent of the total payable corporate income tax of the share of income, depending on the specific type of business activities conducted by the relevant investor in IKN. The relevant facility will be granted for either (i) 25 (twenty-five) years for investment made from 2023 until 2045; or (ii) 20 (twenty) years for investment made from 2036 until 2045; and
-
for foreign tax subject, they shall be exempted from withholding and/or collection of income tax for a period of 10 (ten) years as of the first placement of funds in the financial center at IKN.
Moreover, below are the financial sector business activities in the financial sector in IKN that may obtain the aforementioned facilities:

Types of Financial Sector Business Activities in The Financial Center of IKN
Source: GR No.12/2023.
-
Deduction of Corporate Income Tax for the Establishment and/or Relocation of Head Office and/or Regional Office
This facility shall be granted for business actors with the status of foreign tax subjects who establish and/or relocate their head office and/or regional office in IKN. The deduction of the corporate income tax shall be granted with the following requirements, namely:
-
must have at least 2 (two) related affiliated units and/or business entities outside Indonesia in the form of subsidiaries, business branches, joint ventures, or other similar entities;
-
must have economic substance in IKN; and
-
must establish a legal entity in the form of a limited liability company in Indonesia.
In addition, the deduction of corporate income tax shall also be applicable to domestic taxpayers who establish their head office and/or regional office in IKN on income received or obtained from business actors in IKN or people in IKN. The deduction of corporate income tax shall be applicable with the following requirements, namely:
-
must have economic substance in IKN; and
-
must establish a legal entity in the form of a limited liability company in Indonesia.
The facility of deduction of corporate income tax both for business actors with the status of foreign taxpayers and domestic taxpayers shall be granted for 10 (ten) years at 100% (one hundred percent) of the total payable corporate income tax. Then, the amount of corporate income tac deduction of 50% (fifty percent) of the total payable corporate income tax shall be granted for the following 10 (ten) tax years.
-
Deduction of Gross Income for The Organization of Work Practice, Apprenticeship, and/or Learning Activity in the Context of Fostering and Developing Certain Competency-Based Human Resources
The domestic corporate tax payers that organize and/or involve human resources in education and/or training activities in IKN for the activities of work practice, apprenticeship, and/or learning for the guidance and development of human resources based on certain competencies shall be granted with the facility of deduction of gross income maximum of 250% (two hundred fifty percent) of the total costs incurred for the activities of work, practice, apprenticeship, and/or learning.
The relevant activities that may obtain the above tax facility are activities which are participated by:
-
student, educator, and/or education staff at vocational high school or vocational madrasah aliyah;
-
student, educator, and/or education staff at diploma program university in vocational education;
-
trainee, instructor, and/or coaching staff at job training center; and/or
-
individual who does not have an employment relationship with any party coordinated by the ministry that organizes government affairs in the manpower sector, IKN Authority, provincial governments, or district/city government,
as part of the vocational education curriculum in order to master skills or expertise in a particular field.
-
Deduction of Gross Income for Certain Research and Development Activities
The domestic corporate taxpayers that have domicile and/or business place and conduct certain research and development activities in IKN shall be granted facility in the form of deduction of gross income maximum of 350% (three hundred fifty percent) of the total costs incurred for certain research and development activities which are imposed within a certain period of time. The types of the activities that may obtain the relevant tax facility are research and development activities that are conducted in IKN to produce invention, develop innovation, master new technology, and/or transfer of technology for industrial development to increase the competitiveness of the national industry. The relevant tax facility shall be granted until 2035.
-
Deduction of Gross Income for Donation and/or Costs for the Development of Public Facilities, Social Facilities, and/or Non-Profit Facilities
The facility in the form of deduction of gross income shall be granted for the calculation of taxable income for taxpayers up to a certain amount, a maximum of 200% (two hundred percent) of the total donation and/or costs incurred for the construction of public facilities and/or other non-profit facilities. The donation shall be given in the form of money, goods, and/or costs for the construction of public facilities, social facilities, and/or other non-profit facilities which the relevant facility shall be applicable until 2035.
-
Facility in the Form of Article 21 of Income Tax (PPh Pasal 21) to be Borne by the Government and Final
There are certain conditions of employees who may receive the Article 21 of Income Tax (PPh Pasal 21) to be borne by the Government and is final in nature, namely:
-
receiving or obtaining income from certain employers, namely:
-
employers which have resided, domiciled, or had business activities in IKN;
-
employers which have taxpayer identification number that is registered at the tax service office whose working area covers IKN area or have a tax identity at a place of business activity that is in the area of IKN;
-
have delivered a notification letter of the utilization of the Article 21 of Income tax facility to be borne by the government and final in nature to the Director-General of Tax; and
-
have delivered a report on the realization of the utilization of the Article 21 of Income Tax facility to be borne by the government and final in nature to the Director General of Tax.
-
-
residing in IKN; and
-
holding taxpayer identification registered in tax services office in which its scope of work includes IKN.
There are also some occupations that shall obtain the relevant tax facility, namely state officials, ASN, members of TNI and Polri, who are subject to Article 21 of Income Tax pursuant to the prevailing laws and regulations. The Article 21 of Income Tax to be borne by the Government and final in nature shall remain valid until 2035.
-
Incentives on Final Income Tax for 0% (Zero Percent) on Income from the Gross Turnover of Certain Business of Micro, Small, and Medium Scales Enterprises
Domestic taxpayers in IKN (excluding permanent establishment) that make investment in a value less than Rp10,000,000,000.00 (ten billion rupiah) and meet the following requirements may be subject to final income tax at 0% (zero percent):
-
have resided or domiciled, and/or have a branch in IKN;
-
conduct its business activities in IKN;
-
registered as a taxpayer at the tax service office whose working area covers the area of IKN or have a tax identity at a place of business activity located in IKN;
-
have made investment in IKN and have the qualifications for micro, small, and medium scales enterprises issued by the competent authorities; and
-
have submitted an application to utilize the final income tax facility no later than 3 (three) months after the investment as referred to in point (4) above and obtain approval for the granting of the final income tax facility.
Meanwhile, the final income tax which subject to this facility are those income from business gross turnover of up to Rp50,000,000,000.00 (fifty billion rupiah) in 1 (one) tax year that is received or obtained at a business location located in IKN, excluding the income which is:
-
received or obtained by individual taxpayers from services related to freelance works;
-
received or obtained by corporate taxpayers in the form of limited partnership or firm established by several individual taxpayers who have special expertise in providing similar services to services related to freelance works;
-
from services performed other than in IKN area and/or utilized by service users who live or have their domicile other than in IKN;
-
subject to income tax which is final in nature in accordance with provisions of laws and regulations; and
-
exempted as an object of income tax.
In addition, if the taxpayers have more than 1 (one) business place or branch located in IKN, the limit of the business gross turnover of up to Rp50,000,000,000.00 (fifty billion rupiah) shall be stipulated based on the coverage of all locations of business place or branch of taxpayers located in IKN. The relevant final income tax at 0% (zero percent) should be applicable based on approval from the relevant authority until 2035.
-
Deduction of Income Tax on The Transfer of Land and/or Building Rights
Taxpayers who transfer the land and/or buildings in IKN shall be granted the facility of deduction of income tax of the transfer of land and/or buildings at 100% (one hundred) percent of the amount of payable income tax on the transfer of land and/or buildings rights. This facility is granted for the first acquisition of land and/or buildings rights in IKN to the relevant buyer up to 2035.
Value Added Tax and/or Sales Tax on Luxury Goods
The form of ease of taxation of value added taxes and/or sales tax on luxury goods, as well as the types of activities which are qualified for the relevant facilities until 2035 are as follows:

Forms of Ease of Taxation of Value Added taxes and/or Sales Tax on Luxury Goods and the Relevant Business Activities
Source: GR No. 12/2023.
Customs
The investment facilities related to customs in IKN are in the form of exemption of import duty and import tax facility including the relevant activities which are qualified of such facilities are as follows:

Forms of Custom as investment Facilities in IKN and the Relevant Business Activities
Source: GR No. 12/2023.
The above customs investment facility may be granted until 2045.
Special Tax Facility and Special Revenue for IKN
Special tax and special revenue facility for IKN covers:
-
incentives in the form of special tax deduction, leniency, or exemption for IKN are given by:
-
granting the rights of land in the form of right to cultivate, right to build, and right to use over the right to manage, in which the BPHTB is imposed at a tariff of 0% (zero percent) over the acquisition value for a certain period of time; and
-
granting BPHTB at a tariff of 0% (zero percent) to the party who receives the transfer of right over the said right of land stated in point (1) for certain period of time; and
-
incentives in the form of special revenue deduction, leniency, or exemption for IKN are given by granting a fee of Rp0.00 (zero rupiah) for the issuance of the building approval and worthiness certificate for building.
Facilitation, Provision of Land, Facilities, and Infrastructure for the Implementation of Investment Activities in IKN
The facilitation, provision of land, facility, and infrastructure for the implementation of investment activity in IKN are granted by the Head of IKN Authority which shall include:
-
provision of land or location for business actors;
-
provision of facility and infrastructure;
-
provision of investment convenience and security; and/or
-
ease of access to ready-to-use and skilled manpower.
The Head of IKN Authority shall grant the above facilities based on its priority.
Important Considerations for Prospective Investors in IKN
Beyond the licensing requisites and incentives outlined in Chapter 19.3 and 19.4, several other pivotal considerations should be taken into account when contemplating investments in IKN. These encompass the regulatory framework pertaining to land, provisions for foreign employment facilities, and adherence to housing regulations within IKN.
Land
Land areas in IKN may be designated as state assets and Assets in Control (ADP). Land areas categorized as state assets may be managed by the IKN Authority in accordance with the prevailing laws and regulations. On the other hand, for land areas classified as ADP, the IKN Authority assumes the right-to-manage such lands. Among the IKN Authority’s prerogatives concerning land under its management is the ability to allocate it for specific purposes.
The IKN Authority can allocate land to business actors with attachment of land rights in the form of HGU, HGB, or HP attached to HPL, imposed with 0% (zero percent) of BPHTB, for a certain period. It can also be transferred, inherited, or attached to mortgage rights after the relevant business actor has obtained approval from the IKN Authority. The IKN Authority will provide a guarantee for the certainty of the related land rights period to business actors, and such guarantee shall be written in an agreement (hereinafter referred to as “IKN Land Agreement”). The provision of land rights for business actors in IKN may be divided into two cycles, which are as follows:
-
First Cycle
For business actors, the IKN Authority may provide land rights linked to the right-to-manage (hak atas tanah di atas hak pengelolaan). For the first cycle of land rights possession, these rights may be extended to a maximum of: (i) 95 years for the right-to-cultivate; and (ii) 80 years for both the right-to-build and the right-to-use. These land rights are registered through the issuance of granting right decrees for the relevant rights, and shall be recorded with a land certificate.
Extension and renewal of land rights are granted simultaneously 5 (years) after the relevant land rights are used and/or utilized effectively following the purpose of such land rights.
-
Second Cycle
Approval of land rights’ extension and renewal for the second cycle shall be granted following a joint evaluation between the IKN Authority and the Ministry of Agrarian Affairs and Spatial Planning.
Business entities may request a renewal of the right-to-cultivate for a second cycle within 10 years before the expiration of the first cycle, with a maximum duration of 95 years, in accordance with the relevant land utilization agreement.
Upon the impending expiration of the first cycle of the right-to-build, the option to renew for a second cycle is viable contingent upon the provision of the relevant IKN Land Agreement. Similarly, should the period for conferring the right-to-use during the first cycle draw near its conclusion, the renewal of the right-to-use for a second cycle may be pursued in accordance with the applicable IKN Land Agreement.
It is imperative to also consider provisions which apply to specific circumstances. For example, if a right-to-build is granted for the construction of a building that will be transferred to the public, then after obtaining prior approval from the IKN Authority: (i) for the standard houses, the right-to-build can be upgraded to freehold title; or (ii) for apartment units, the freehold title is given to each unit. Specific for foreign national residential houses, they shall be given the right-to-use attached to the right-to-manage.
Foreign Employment
Foreign workers utilization plan validation may be given for 10 (ten) years and is extendable. Furthermore, foreign workers may be permitted to stay 10 (ten) years. This may be extendable in accordance with the workers’ contract.
Exemption of compensation fund payment for the usage of foreign workers may be provided for: (i) institutions such as Government agencies, international agencies, social institutions, and religious institutions; and (ii) utilization of foreign workers by businesses carrying out Government-owned strategic projects in IKN.
Shareholders serving as part of management of its companies may be granted residence permits in accordance with their term as part of the management.
Housing
The implementation of housing and residential area in IKN region is based on the following zones, namely (i) simple housing; (ii) middle housing; and (iii) real estate. To accelerate the development and procurement of housing and residential area for residents in IKN, business actors in the housing and settlement sector who have not yet fulfilled their balanced housing obligations in other regions may do so in the Nusantara Capital City area, with due consideration to the detailed plans and spatial planning of the Nusantara Capital City. Such obligations shall be fulfilled through application to IKN Authority with options of (i) conducting balanced housing development in IKN region; or (ii) paying conversion fees for the fulfilment of balanced housing.
The application to the Head of IKN Authority shall be conveyed by providing self-statement on balanced housing obligation. Upon the application submitted by the business actors, the Head of IKN Authority shall coordinate with MoHRA and MoHA. Further, the Head of the IKN Authority shall report the fulfilment of the balanced housing obligation at least once a year to the MoHRA and the MoHA.
Specifically, in accordance with Article 25 (7) GR 12/2023, business actors fulfilling the balanced housing obligation will be granted incentives, which may include:
-
assistance for housing development programs;
-
tax relief for modest housing in accordance with applicable regulations;
-
assistance for infrastructure, facilities, and public utilities;
-
facilitation in obtaining land for housing development and its expansion;
-
support for accessibility to balanced housing locations within the Nusantara Capital area;
-
exemption from BPHTB (Property Transfer Duty);
-
reduction of PBB for a specified period; and/or
-
award for contributions to balanced housing.
BPHTB exemptions and PBB reductions are also apply to consumers. Lastly, BPHTB exemptions and PBB reductions for a specified period will be proposed by the Head of the Nusantara Capital Authority for approval by the Regent of Penajam Paser Utara or the Regent of Kutai Kartanegara, depending on the jurisdiction, until the establishment of the Special Regional Government of the Nusantara Capital City.




















